EEPROM Data memory
PIC16F84 has 64 bytes of EEPROM memory locations on addresses from 00h to 63h that can be written to or read from. The most important characteristic of this memory is that it does not lose its contents with the loss of power supply. Data can be retained in EEPROM without power supply for up to 40 years (as manufacturer of PIC16F84 microcontroller states), and up to 1 million cycles of writing can be executed.
In practice, EEPROM memory is used for storing important data or process parameters.
One such parameter is a given temperature, assigned when setting up a temperature regulator to some process.
If that data wasn't retained, it would be necessary to adjust a given temperature after each loss of supply. Since this is very impractical (and even dangerous),
manufacturers of microcontrollers have began installing one smaller type of EEPROM
memory.
EEPROM memory is placed in a special memory space and can be accessed through special registers. These registers are:
| EEDATA | Holds read data or that to be written. |
| EEADR | Contains an address of EEPROM location being accessed. |
| EECON1 | Contains control bits. |
| EECON2 | This register does not exist physically and serves to protect EEPROM from accidental writing. |
EECON1 register is a control register with five implemented
bits.
Bits 5, 6 and 7 are not used, and by reading always are zero. Interpretation of EECON1 register bits follows.
EECON1 Register
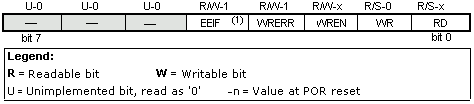
bit 4 EEIF (EEPROM Write Operation Interrupt Flag bit) Bit used to inform that writing data to EEPROM has ended.
When writing has terminated, this bit would be set automatically. Programmer must
clear EEIF bit in his program in order to detect new termination of writing.
1 = writing terminated
0 = writing not terminated yet, or has not started
bit 3 WRERR (Write EEPROM Error Flag) Error during writing to EEPROM
This bit was set only in cases when writing to EEPROM had been
interrupted by a reset signal or by running out of time in watchdog timer
(if activated).
1 = error occurred
0 = error did not occur
bit 2 WREN (EEPROM Write Enable bit) Enables writing to EEPROM
If this bit was not set, microcontroller would not allow writing to EEPROM.
1 = writing allowed
0 = writing disallowed
bit 1 WR (Write Control bit)
Setting of this bit initializes writing data from EEDATA register to the address
specified trough EEADR register.
1 = initializes writing
0 = does not initialize writing
bit 0 RD (Read Control bit)
Setting this bit initializes transfer of data from address defined in EEADR to EEDATA register. Since time is not as essential in reading data as in writing, data from EEDATA can already be used further in the next instruction.
1 = initializes reading
0 = does not initialize reading
Reading from EEPROM Memory
Setting the RD bit initializes transfer of data from address found in EEADR register to EEDATA register. As in reading data we don't need so much time as in writing, data taken over from EEDATA register can already be used further in the next instruction.
Sample of the part of a program which reads data in EEPROM, could look something like the following:
BCF STATUS, RPO ; bankO, because EEADR is at 09h
MOVLW 0X00 ; address of location being read
MOVWF EEADR ; address transferred to EEADR
BSF STATUS, RPO ; bankl because EECONl is at 88h
BSF EECON1, RD ; reading from EEPROM
BCF STATUS, RPO ; BankO because EEDATA is at 08h
MOVF EEDATA, W ; W <— EEDATA
After the last program instruction, contents from an EEPROM address zero can be found in working register w.
Writing to EEPROM Memory
In order to write data to EEPROM location, programmer must first write address to EEADR register and data to EEDATA register. Only then is it useful to set WR bit which sets the whole action in motion. WR bit will be reset, and EEIF bit set following a writing what may be used in processing interrupts. Values 55h and AAh are the first and the second key whose disallow for accidental writing to EEPROM to occur. These two values are written to EECON2 which serves only that purpose, to receive these two values and thus prevent any accidental writing to EEPROM memory. Program lines marked as 1, 2, 3, and 4 must be executed in that order in even time intervals. Therefore, it is very important to turn off interrupts which could change the timing needed for executing instructions. After writing, interrupts can be enabled again .
Example of the part of a program which writes data 0xEE to first location in EEPROM memory could look something like the following:
BCF STATUS, RPO ;bankO, because EEADR is at 09h
MOVLW 0X00 ;address of location being written to
MOVWF EEADR ;address being transferred to EEADR
MOVLW OXEE ;rarite the value OxEE
MOVWF EEDATA ;data goes to EEDATA register
BSF STATUS, RPO ;Bankl because EEADR is at 09h
BCF INTCON, GIE ;all interrupts are disabled
BSF EEC0N1, UREN ;writing enabled
MOVLW 55H
1) MOVWF EECON2 ;first key 55h -> EECON2
2) MOVLW AAH
3) MOVWF EECON2 ;second key AAh -> EECON2
4) BSF EEC0N1,UR ;initializes writing
BSF INTCON, GIE ;interrupts are enabled
|
|
It is recommended that WREN be turned off the whole time except when writing data to EEPROM, so that possibility of accidental writing would be minimal. All writing to EEPROM will automatically clear a location prior to writing a new! |
User Comments
No Posts found !Login to Post a Comment.